Menopause’s Effect On Hair can be extreme and it’s important to know all about it. Menopause is a normal biological process that occurs when a woman’s reproductive years come to an end. It usually happens around the age of 50, however the precise time might vary. Hormonal changes during menopause can have a variety of consequences on the body, including the hair.It’s crucial to understand that the effects of menopause on hair might vary greatly amongst people. Furthermore, not all women’s hair changes much at this era. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, which includes a well-balanced diet, frequent exercise, and stress management, can help with general well-being and may help to reduce some of the impacts on hair.
Table of Contents
Menopause’s Effect On Hair Health
Hormonal Changes
A crucial component during menopause is a drop in estrogen levels, a hormone that plays a role in maintaining hair thickness and development. Furthermore, androgen hormone levels may rise, which can lead to hair loss.
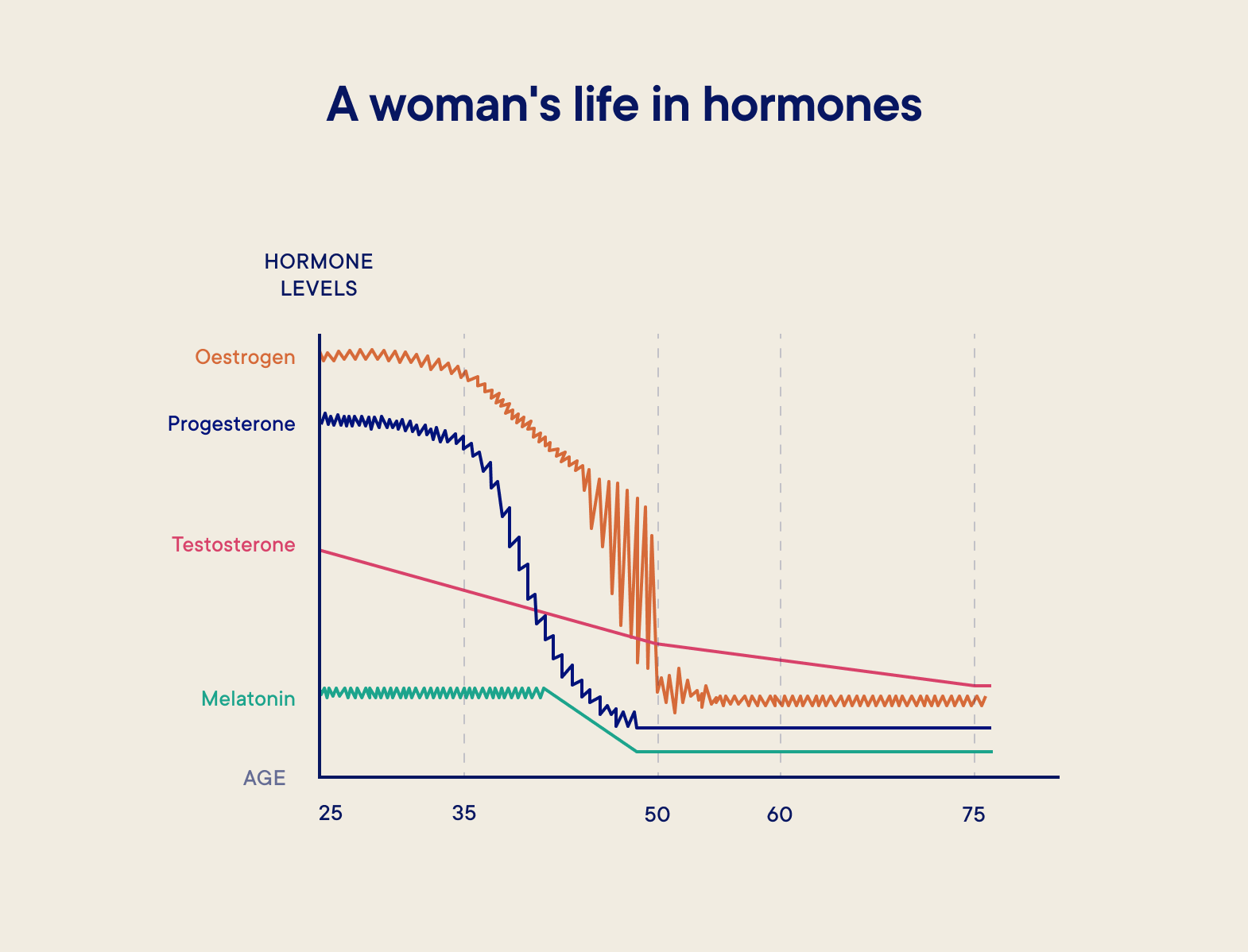
Hair Thinning & Reduced Hair Density
Thinning hair is one of the most apparent side effects of menopause. Reduced estrogen levels can cause a decrease in the width of individual hair strands, resulting in a thinner overall look. Menopausal hormone changes can also cause a decrease in hair density, which reduces the number of hair follicles actively creating new hair. This might contribute to a reduction of overall hair volume.
Changes in Hair Texture & Increased Hair Loss
During menopause, some women may have increased shedding or hair loss. This is due to hormonal changes and the susceptibility of hair follicles to androgen hormones. Menopause can cause changes in hair texture. Some women may find their hair becoming dry, brittle, or prone to breaking.
Onset or Exacerbation of Hair Conditions
Menopause can occasionally cause or aggravate pre-existing hair disorders like alopecia areata or female pattern baldness. The appearance of these disorders is influenced by genetics and individual health variables.
Slower Hair Growth
During menopause, the natural hair growth cycle may slow down, resulting in a prolonged resting period (telogen) and a shorter growth phase (anagen). This might cause hair regrowth to be sluggish.
Scalp Changes
Menopausal hormone changes may have an impact on scalp health, resulting in variations in oil production. Some women may report their scalp becoming drier, while others may perceive an increase in oiliness.

How to Ensure Hair Health After Menopause
Maintaining hair health after menopause necessitates a comprehensive strategy that includes hormonal changes, dietary requirements, and adequate hair care. It is important to remember that hair changes during and after menopause are a normal part of the aging process. Adopting a healthy lifestyle and practicing these guidelines, on the other hand, can assist maintain optimal hair health and handle any issues you may have.Here are some suggestions for maintaining hair health throughout and after menopause.
- Balanced Diet: Proteins, vitamins (particularly B vitamins and vitamin E), minerals (iron and zinc), and omega-3 fatty acids are all important for hair health. Consider seeking specialized dietary guidance from a dietitian.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your body and hair moisturized. Proper hydration promotes overall hair health and helps to avoid dryness.

- Stress Management: Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga are all stress-relieving strategies. Chronic stress can lead to hair problems, and stress management is essential for general well-being.
- Gentle hair Care: To avoid depleting the hair of its natural oils, use moderate, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners. Excessive heat styling and severe chemical treatments can cause dryness hair breakage.
- Supplements: Consult your physician about the possible advantages of supplements such as biotin, omega-3 fatty acids, and other vitamins and minerals that promote hair health. Do not self-prescribe supplements unless you have received expert advice.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Hormone replacement treatment may be recommended for certain women to correct hormonal abnormalities during menopause. Consult your healthcare practitioner about the possible advantages and hazards.
- Avoid Excessive Smoking and Alcohol: Tobacco use and excessive alcohol use can have a harmful influence on hair health. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol use can improve general health, including hair health.
- Dermatologist Consultation: Consider contacting a dermatologist or a healthcare practitioner who specializes in hair health if you detect substantial changes in your hair or scalp. They can examine your specific requirements and offer specialized advise or treatments.
- Protective Hair Styles: Consider protective hairstyles like braids, buns, or loose ponytails that reduce friction and damage to the hair. Avoid pulling on the hair and stressing the follicles with tight hairstyles.
- Regular trims: Schedule frequent haircuts to avoid split ends and keep your hair healthy. This method can also make your hair appear thicker and healthier.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood circulation, which aids in the supply of nutrients to hair follicles. Exercise also aids with stress reduction.

